# Visual Intertial Odometry (VIO)
Visual Inertial Odometry (VIO) is a computer vision technique used for estimating the 3D pose (local position and orientation) and velocity of a moving vehicle relative to a local starting position. It is commonly used to navigate a vehicle in situations where GPS is absent or unreliable (e.g. indoors, or when flying under a bridge).
VIO uses Visual Odometry to estimate vehicle pose from camera images, combined with inertial measurements from the vehicle IMU (to correct for errors associated with rapid vehicle movement resulting in poor image capture).
This topic shows how to set up PX4 and a companion computer to use the supported VIO setup.
{% youtube %} https://youtu.be/gWtrka2mK7U {% endyoutube %}
Tip The Auterion product video above shows a vehicle flying using the supported setup.
Note This (supported) solution uses ROS for routing VIO information to PX4. PX4 itself does not care about the source of messages, provided they are provided via the appropriate MAVLink Interface.
# Supported Setup {#supported_setup}
The supported setup uses the T265 Intel Realsense Tracking Camera and ROS (running on a companion computer) to supply odometry information to PX4. The Auterion VIO bridge ROS node provides a bridge between this (particular) camera and ROS.
# Camera Mounting
Attach the camera to the companion computer and mount it to the frame:
- Connect the T265 Intel Realsense Tracking Camera using the supplied cable.
- Mount the camera with lenses pointing down if at all possible (default).
- The camera is very senstive to vibration; a soft mounting is recommended (e.g. using vibration isolation foam).
# ROS/VIO Setup
To setup the Bridge, ROS and PX4:
On the companion computer, install and configure MAVROS.
Get the Auterion VIO bridge ROS node:
- Clone this repository in your catkin workspace.
cd ~/catkin_ws/src git clone https://github.com/Auterion/VIO.git - Build the package:
cd ~/catkin_ws/src catkin build px4_realsense_bridge
- Clone this repository in your catkin workspace.
Configure the camera orientation if needed:
- The VIO bridge doesn't require any configuration if the camera is mounted with the lenses facing down (the default).
- For any other orientation modify bridge_mavros.launch in the section below:
<node pkg="tf" type="static_transform_publisher" name="tf_baseLink_cameraPose" args="0 0 0 0 1.5708 0 base_link camera_pose_frame 1000"/>
This is a static transform that links the camera ROS frame
camera_pose_frameto the mavros drone framebase_link.- the first three
argsspecify translation x,y,z in metres from the center of flight controller to camera. For example, if the camera is 10cm in front of the controller and 4cm up, the first three numbers would be : [0.1, 0, 0.04,...] - the next three
argsspecify rotation in radians (yaw, pitch, roll). So[... 0, 1.5708, 0]means pitch down by 90deg (facing the ground). Facing straight forward would be [... 0 0 0].
Follow the instructions below for tuning the PX4 EKF2 estimator.
Run VIO by calling
roslaunchwith an appropriate launch file:cd ~/catkin_ws/src roslaunch px4_realsense_bridge bridge_mavros.launchThe launch file options are:
- bridge_mavros.launch: Use on vehicle in most cases (starts bridge and MAVROS).
- bridge.launch: Use if some other component is responsible for starting MAVROS (only starts bridge)
- bridge_mavros_sitl.launch:Use for simulation (starts bridge, MAVROS, SITL)
Verify the connection to the flight controller.
Tip You can use the QGroundControl MAVLink Inspector to verify that you're getting
ODOMETRYorVISION_POSITION_ESTIMATEmessages (or check forHEARTBEATmessages that have the component id 197 (MAV_COMP_ID_VISUAL_INERTIAL_ODOMETRY)).Verify that VIO is Setup Correctly before your first flight!
# PX4 Tuning {#ekf2_tuning}
The following parameters must be set to use external position information with EKF2.
| Parameter | Setting for External Position Estimation |
|---|---|
| EKF2_AID_MASK | Set vision position fusion, vision velocity fusion, vision yaw fusion and external vision rotation accoring to your desired fusion model. |
| EKF2_HGT_MODE | Set to Vision to use the vision a primary source for altitude estimation. |
| EKF2_EV_DELAY | Set to the difference between the timestamp of the measurement and the "actual" capture time. For more information see below. |
| EKF2_EV_POS_X, EKF2_EV_POS_Y, EKF2_EV_POS_Z | Set the position of the vision sensor with respect to the vehicles body frame. |
These can be set in QGroundControl > Vehicle Setup > Parameters > EKF2 (remember to reboot the flight controller in order for parameter changes to take effect).
For more detailed/additional information, see: ECL/EKF Overview & Tuning > External Vision System.
# Tuning EKF2_EV_DELAY {#tuning-EKF2_EV_DELAY}
EKF2_EV_DELAY is the Vision Position Estimator delay relative to IMU measurements. In other words, it is the difference between the vision system timestamp and the "actual" capture time that would have been recorded by the IMU clock (the "base clock" for EKF2).
Technically this can be set to 0 if there is correct timestamping (not just arrival time) and timesync (e.g NTP) between MoCap and (for example) ROS computers. In reality, this may need some empirical tuning becuase delays in the communication chain are very setup-specific. It is rare that a system is setup with an entirely synchronised chain!
A rough estimate of the delay can be obtained from logs by checking the offset between IMU rates and the EV rates:
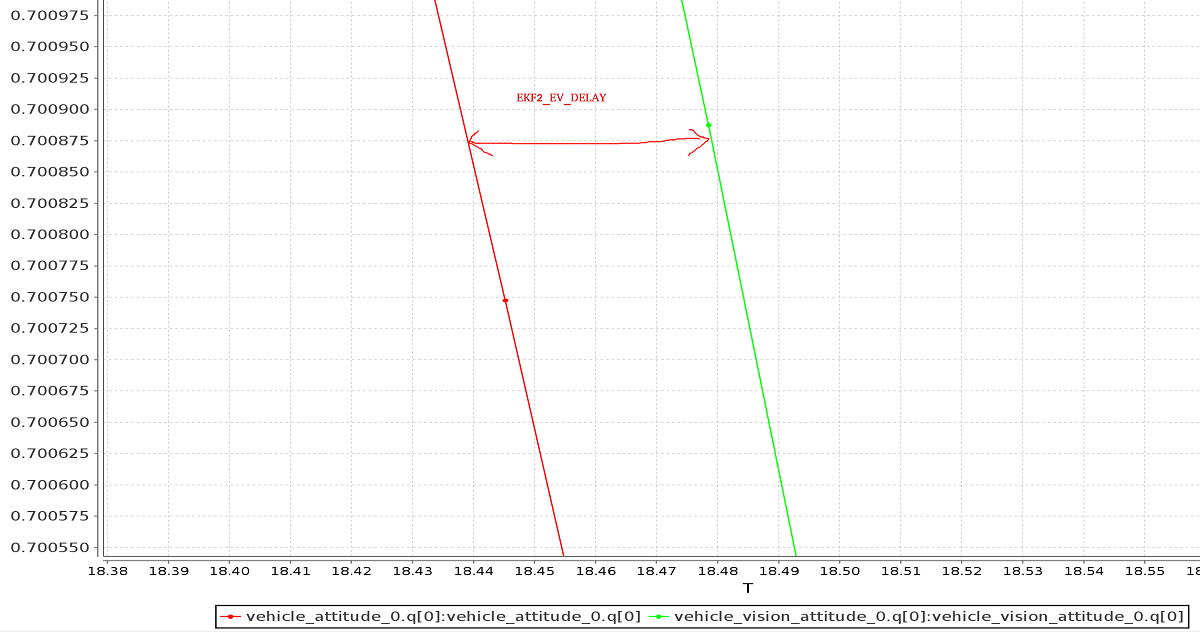
Note A plot of external data vs. onboard estimate (as above) can be generated using FlightPlot or similar flight analysis tools.
The value can further be tuned by varying the parameter to find the value that yields the lowest EKF innovations during dynamic maneuvers.
# Check/Verify VIO Estimate {#verify_estimate}
Perform the following checks to verify that VIO is working properly before your first flight:
- Set the PX4 parameter
MAV_ODOM_LPto 1. PX4 will then stream back the received external pose as MAVLink ODOMETRY messages. You can check these MAVLink messages with the QGroundControl MAVLink Inspector - Yaw the vehicle until the quaternion of the
ODOMETRYmessage is very close to a unit quaternion (w=1, x=y=z=0).- At this point the body frame is aligned with the reference frame of the external pose system.
- If you do not manage to get a quaternion close to the unit quaternion without rolling or pitching your vehicle, your frame probably still has a pitch or roll offset. Do not proceed if this is the case and check your coordinate frames again.
- Once aligned you can pick the vehicle up from the ground and you should see the position's z coordinate decrease. Moving the vehicle in forward direction, should increase the position's x coordinate. While moving the vehicle to the right should increase the y coordinate.
- Check that linear velocities in the message are in expressed in the FRD body frame reference frame.
- Set the PX4 parameter
MAV_ODOM_LPback to 0. PX4 will stop streaming theODOMETRYmessage back.
If those steps are consistent, you can try your first flight:
Put the vehicle on the ground and start streaming
ODOMETRYfeedback (as above). Lower your throttle stick and arm the motors.At this point, with the left stick at the lowest position, switch to position control. You should have a green light. The green light tells you that position feedback is available and position control is now activated.
Put the throttle stick in the middle (the dead zone) so that the vehicle maintains its altitude. Raising the stick will increase the reference altitude while lowering the value will decrease it. Similarly the other stick will change position over ground.
Increase the value of the throttle stick and the vehicle will take off, put it back to the middle right after.
Confirm that the vehicle can hold its position.
# Troubleshooting
First make sure MAVROS is able to connect successfully to the flight controller.
If it is connecting properly common problems/solutions are:
Problem: I get drift / flyaways when the drone flies, but not when I carry it around with the props off.
- If using the T265 try soft-mounting it (this camera is very sensitive to high frequency vibrations).
Problem: I get toilet-bowling when VIO is enabled.
- Make sure the orientation of the camera matches the transform in the launch file. Use the QGroundControl MAVLink Inspector to verify that the velocities in the
ODOMETRYmessage coming from MAVROS are aligned to the FRD coordinate system.
- Make sure the orientation of the camera matches the transform in the launch file. Use the QGroundControl MAVLink Inspector to verify that the velocities in the
Problem: I want to use vision position to do loop closing, and also want to run GPS.
- This is really difficult, because when they disagree it will confuse the EKF. From testing it is more reliable to just use vision velocity (if you figure out a way to make this configuration reliable, let us know).
# Developer Information
Developers who are interested in extending this implementation (or writing a different one, which might not depend on ROS) should see Using Vision or Motion Capture Systems for Position Estimation (PX4 Developer Guide).
This topic also explains how to configure VIO for use with the LPE Estimator (deprecated).