PX4 Vision Autonomy Development Kit
[PX4 Vision Autonomy Development Kit] (https://holybro.com/collections/multicopter-kit/PX4-Vision) - це надійний і недорогий комплект для створення систем комп'ютерного зору на автономних пристроях.
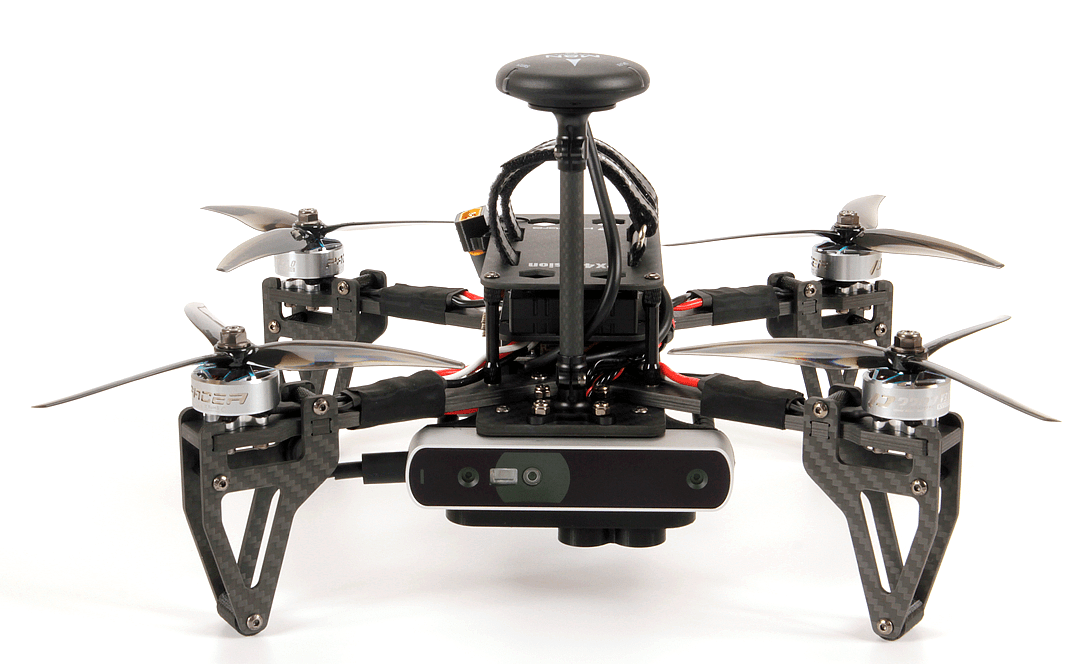
Комплект містить майже готовий до польоту квадрокоптер з вуглецевого волокна, оснащений польотним контролером Pixhawk 4 або Pixhawk 6C (на версії 1.5), комп'ютером-компаньйоном UP Core (4 ГБ пам'яті та 64 ГБ eMMC), а також камерою глибини Occipital Structure Core .
:::note Цей пристрій не має попередньо встановленого програмного забезпечення. До комплекту входить карта пам'яті USB з прикладом реалізації функції уникнення перешкод, на основі проекту PX4 Avoidance. Цей приклад є орієнтовним і слугує для демонстрації можливостей платформи. Програмне забезпечення не сумісне з останньою версією PX4, а також не підтримується і не обслуговується. :::
Посібник надає інформацію про мінімальне додаткове налаштування, потрібне для того, щоб підготувати апарат до польоту (встановлення системи дистанційного керування та акумулятора). Він також описує перший політ і те, як почати модифікацію коду комп'ютерного зору.
Де купити
Зміст посібника Px4 Vision Guide
- Попередження та сповіщення
- Що всередині
- Що ще вам потрібно
- Первинне налаштування
- Керування дроном з запобіганням зіткнень
- Розробка з використанням комплекту
- Розпіновка плати PX4 Vision Carrier
- Інші ресурси для розробників
- Як отримати технічну підтримку
Попередження та сповіщення
Комплект призначений для проєктів комп'ютерного зору, які використовують камеру, спрямовану вперед (він не має камер глибини, спрямованих вниз або назад). Отже, його не можна використовувати (без модифікації) для тестування [Безпечної посадки] (../computer_vision/safe_landing.md) або інших функцій, для яких потрібна камера, спрямована вниз.
Уникання перешкод у місіях можна тестувати лише за наявності сигналу GPS (місії використовують GPS-координати). Запобігання зіткненням можна перевірити в режимі позиціювання за умови, що є стійке захоплення позиції, отримане або з GPS, або з оптичного потоку.
Порт, позначений
USB1, може глушити GPS, якщо його використовувати з периферійним пристроєм USB3 (вимкніть GPS-залежні функції, зокрема місії). Саме тому образ завантаження постачається на флешці USB2.0.PX4 Vision v1 з ECN 010 або вище (несуча плата RC05 і вище), UP Core може живитися як від розетки постійного струму, так і від акумулятора.
Всі PX4 Vision v1.5 UP Core можна живити як від мережі постійного струму, так і від батареї.
WARNING
For PX4 Vision v1 with ECN below 010/carrier board below RC04, the UP Core should only be powered using the battery (do not remove the UP Core power socket safety cover). This does not apply to PX4 Vision v1.5
Що всередині
:::note Відмінності між PX4 Vision V1 і V1.5 можна знайти тут :::
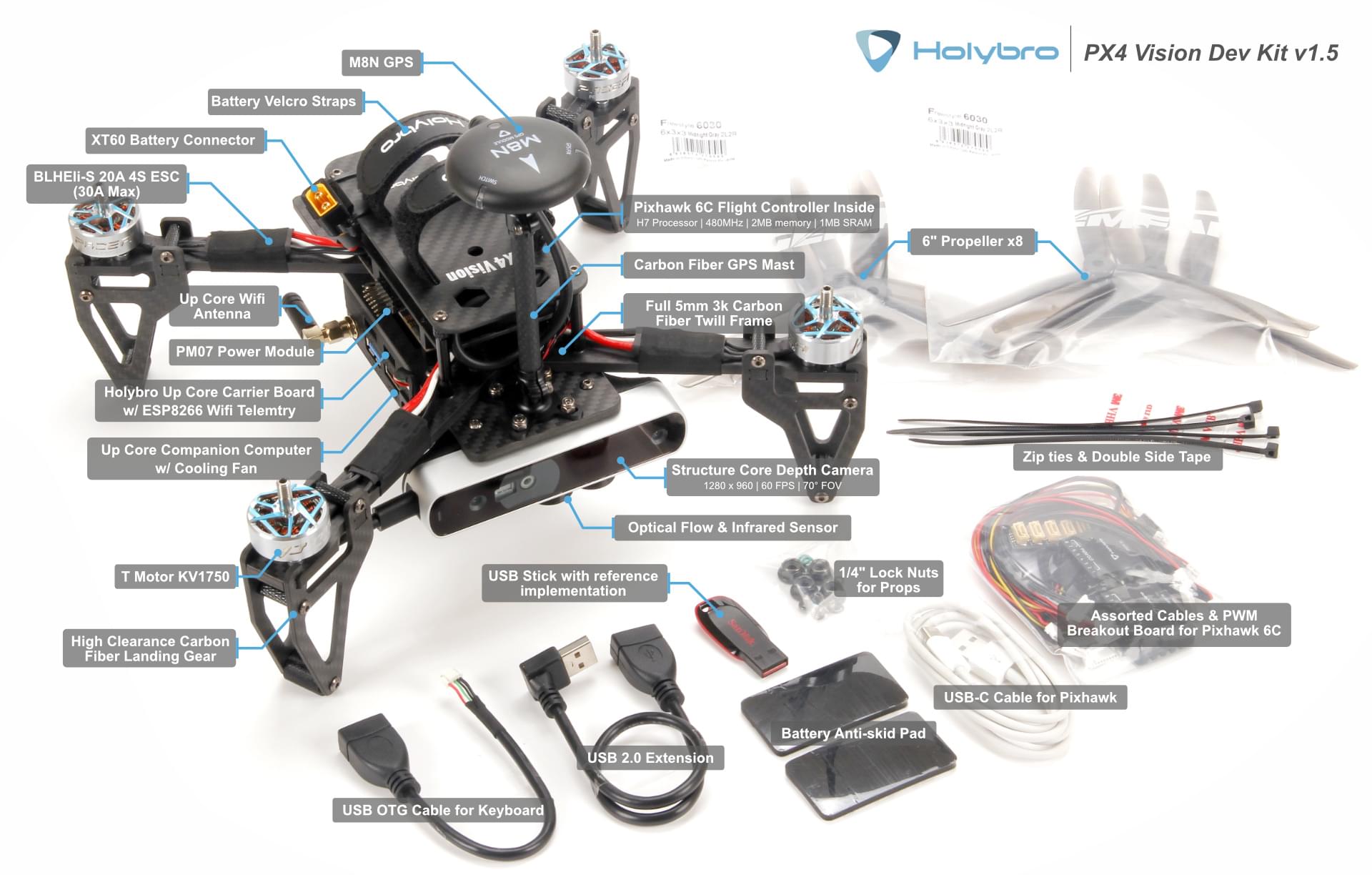

Про те, що знаходиться всередині PX4 Vision V1, можна дізнатися тут [PX4 v1.13 Docs here] (https://docs.px4.io/v1.13/en/complete_vehicles/px4_vision_kit.html#what-is-inside).
PX4 Vision DevKit містить наступні компоненти:
Основні компоненти:
- 1x Pixhawk 4 або Pixhawk 6C (для v1.5) польотний контролер
- 1x оптичний датчик потоку PMW3901
- 1x датчик відстані TOF інфрачервоного діапазону (PSK‐CM8JL65‐CC5)
- 1x камера глибини Structure Core
- Камера з широким кутом огляду 160 градусів
- Стерео-інфрачервоні камери
- Вбудований ІМП (інерціальний модуль)
- Потужний багатоядерний процесор глибини NU3000
- 1x комп'ютер UP Core (4 ГБ оперативної пам'яті та 64 ГБ eMMC з Ubuntu та PX4 униканням)
- Intel® Atom™ x5-z8350 (до1.92 GHz)
- Сумісні ОС: повна версія Microsoft Windows 10, Linux (ubilinux, Ubuntu, Yocto), Android
- FTDI UART підключений до контролера польоту
USB1: USB3.0 Порт, який використовується для завантаження середовища уникнення PX4 з флешки USB2.0 (підключення периферійного пристрою USB3.0 може заглушити GPS).USB2: Порт USB2.0 на роз'ємі JST-GH. Може бути використаний для другої камери, LTE тощо (або клавіатури/миші під час розробки).USB3: Порт USB2.0 JST-GH, підключений до камери глибиниHDMI: HDMI вихід- SD карта
- WiFi 802.11 b/g/n @ 2,4 ГГц (підключений до зовнішньої антени №1). Дозволяє комп'ютеру отримати доступ до домашньої WiFi-мережі для доступу до Інтернету та оновлень.
Механічні характеристики:
- Каркас: Цілісна 5-міліметрова саржа з вуглецевого волокна 3k
- Мотори: T-MOTOR KV1750
- ESC: BEHEli-S 20A ESC
- GPS: M8N GPS модуль
- Модуль живлення: Holybro PM07
- Колісна база: 286мм
- Вага: 854 грами без акумулятора або гвинтів
- Телеметрія: ESP8266 підключений до польотного контролера (приєднаний до зовнішньої антени №2). Вмикає бездротове з'єднання з наземною станцією.
Флеш-накопичувач USB2.0 з попередньо завантаженим програмним забезпеченням, яке включає в себе:
- Ubuntu 18.04 LTS
- ROS Melodic
- Occipital Structure Core ROS драйвер
- MAVROS
- PX4 Avoidance
Різноманітні кабелі, 8x гвинти, 2x ремінці для акумулятора (встановлені) та інші аксесуари (їх можна використовувати для підключення додаткових периферійних пристроїв).
Що ще потрібно
Комплект містить усе необхідне обладнання для керування дроном, окрім акумулятора та системи радіоуправління, які необхідно придбати окремо:
- Батарея:
- 4S LiPo з гніздом XT60
- Довжина менше 115 мм (щоб поміститися між роз'ємом живлення та GPS-антеною)
- Системи радіо керування
- Будь-яка PX4-сумісна RC система може бути використана.
- Передавач FrSky Taranis з приймачем R-XSR - одна з найпопулярніших комбінацій.
- Шестигранний ключ H2.0 (для відкручування верхньої панелі, з метою підключення пульта дистанційного керування)
In addition, users will need ground station hardware/software:
- Laptop or tablet running QGroundControl (QGC).
First-time Setup
Attach a compatible RC receiver to the vehicle (not supplied with kit):
- Remove/unscrew the top plate (where the battery goes) using an H2.0 hex key tool.
- Connect the receiver to the flight controller.
- Re-attach the top plate.
- Mount the RC receiver on the UP Core carrier board plate at the back of the vehicle (use zipties or double-sided tape).
- Ensure the antennas are clear of any obstructions and electrically isolated from the frame (e.g. secure them under the carrier board or to the vehicle arms or legs).
Bind the RC ground and air units (if not already done). The binding procedure depends on the specific radio system used (read the receiver manual).
Raise the GPS mast to the vertical position and screw the cover onto the holder on the base plate. (Not required for v1.5)
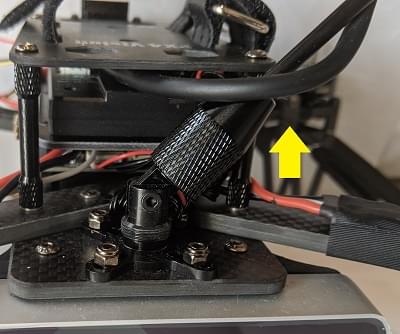
Insert the pre-imaged USB2.0 stick from the kit into the UP Core port labeled
USB1(highlighted below).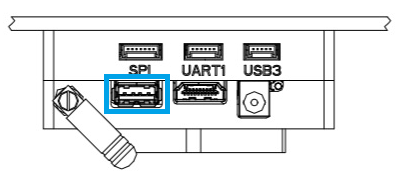
Power the vehicle with a fully charged battery. :::note Ensure propellers are removed before connecting the battery.
:::
Connect the ground station to the vehicle WiFi network (after a few seconds) using the following default credentials:
- SSID: pixhawk4
- Password: pixhawk4
TIP
WiFi network SSID, password, and other credentials may be changed after connecting (if desired), by using a web browser to open the URL:
http://192.168.4.1. The baud rate must not be changed from 921600.
:::
Start QGroundControl on the ground station.
Configure/calibrate the vehicle:
:::note The vehicle should arrive pre-calibrated (e.g. with firmware, airframe, battery, and sensors all setup). You will however need to calibrate the radio system (that you just connected) and it is often worth re-doing the compass calibration.
:::
(Optional) Configure a Flight Mode selector switch on the remote controller.
:::note Modes can also be changed using QGroundControl
:::
We recommend RC controller switches are define for:
- Position Mode - a safe manual flight mode that can be used to test collision prevention.
- Mission Mode - run missions and test obstacle avoidance.
- Return Mode - return vehicle safely to its launch point and land.
Attach the propellers with the rotations as shown:
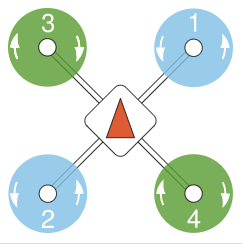
The propellers directions can be determined from the labels: 6045 (normal, counter-clockwise) and 6045R (reversed, clockwise).

Screw down firmly using the provided propellor nuts:
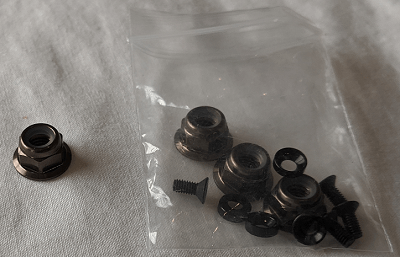
Fly the Drone with Avoidance
When the vehicle setup described above is complete:
Connect the battery to power the vehicle.
Wait until the boot sequence completes and the avoidance system has started (the vehicle will reject arming commands during boot).
TIP
The boot/startup process takes around 1 minute from the supplied USB stick (or 30 seconds from internal memory).
:::
Check that the avoidance system has started properly:
The QGroundControl notification log displays the message: Avoidance system connected.
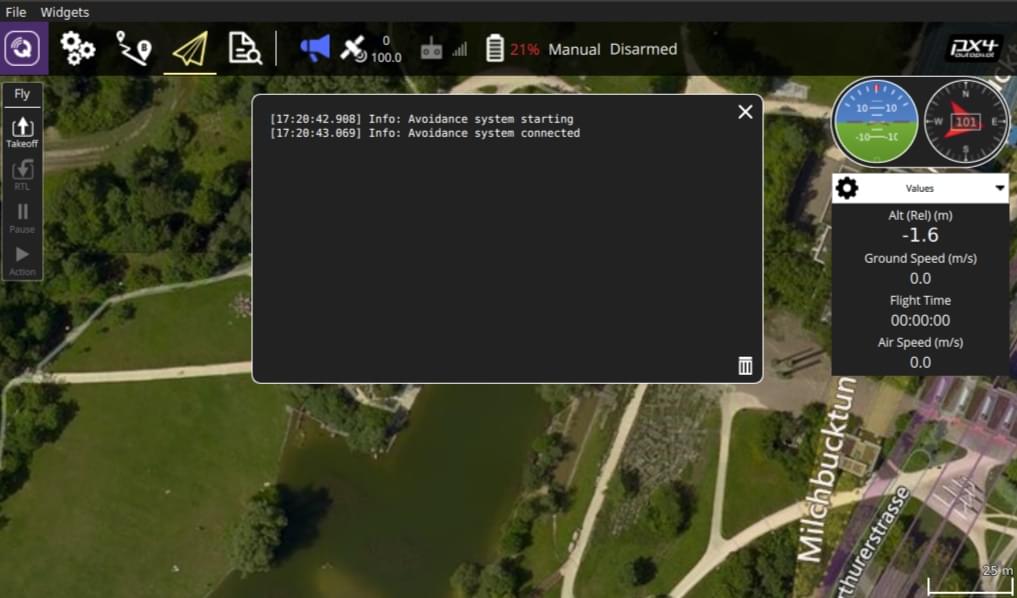
A red laser is visible on the front of the Structure Core camera.
Wait for the GPS LED to turn green. This means that the vehicle has a GPS fix and is ready to fly!
Connect the ground station to the vehicle WiFi network.
Find a safe outdoor location for flying, ideally with a tree or some other convenient obstacle for testing PX4 Vision.
To test collision prevention, enable Position Mode and fly manually towards an obstacle. The vehicle should slow down and then stop within 6m of the obstacle (the distance can be changed using the CP_DIST parameter).
To test obstacle avoidance, create a mission where the path is blocked by an obstacle. Then switch to Mission Mode to run the mission, and observe the vehicle moving around the obstacle and then returning to the planned course.
Development using the Kit
The following sections explain how to use the kit as an environment for developing computer vision software.
PX4 Avoidance Overview
The PX4 Avoidance system consists of computer vision software running on a companion computer (with attached depth camera) that provides obstacle and/or route information to the PX4 flight stack running on a flight controller.
Documentation about the companion computer vision/planning software can be found on github here: PX4/PX4-Avoidance. The project provides a number of different planner implementations (packaged as ROS nodes):
- The PX4 Vision Kit runs the localplanner by default and this is the recommended starting point for your own software.
- The globalplanner has not been tested with this kit.
- The landing planner requires a downward facing camera, and cannot used without first modifying the camera mounting.
PX4 and the companion computer exchange data over MAVLink using these interfaces:
- Path Planning Interface - API for implementing avoidance features in automatic modes.
- Collision Prevention Interface - API for vehicle based avoidance in manual position mode based on an obstacle map (currently used for collision prevention).
Installing the image on the Companion Computer
You can install the image on the UP Core and boot from internal memory (instead of the USB stick).
This is recommended because booting from internal memory is much faster, frees up a USB port, and may well provide more memory than your USB stick.
:::note Booting from internal memory takes around 30 seconds while booting from the supplied USB2 stick boots in about a minute (other cards may take several times longer). :::
To flash the USB image to the UP Core:
Insert the pre-flashed USB drive into the UP Core port labeled
USB1.Login to the companion computer (as described above).
Open a terminal and run the following command to copy the image onto internal memory (eMMC). The terminal will prompt for a number of responses during the flashing process.
shcd ~/catkin_ws/src/px4vision_ros/tools sudo ./flash_emmc.sh:::note All information saved in the UP Core computer will be removed when executing this script.
:::
Pull out the USB stick.
Restart the vehicle. The UP Core computer will now boot from internal memory (eMMC).
Boot the Companion Computer
First insert the provided USB2.0 stick into the UP Core port labeled USB1, and then power the vehicle using a 4S battery. The avoidance system should start within about 1 minute (though this does depend on the USB stick supplied).
TIP
Fly the Drone with Avoidance additionally explains how to verify that the avoidance system is active.
If you've already installed the image on the companion computer you can just power the vehicle (i.e. no USB stick is needed). The avoidance system should be up and running within around 30 seconds.
Once started the companion computer can be used both as a computer vision development environment and for running the software.
Login to the Companion Computer
To login to the companion computer:
Connect a keyboard and mouse to the UP Core via port
USB2: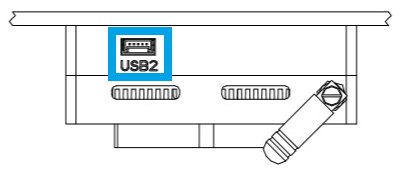
Use the USB-JST cable from the kit to get a USB A connector

A USB hub can be attached to the cable if the keyboard and mouse have separate connectors.
Connect a monitor to the UP Core HDMI port.
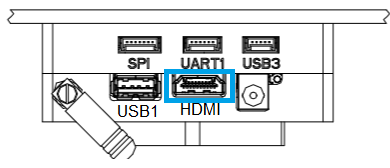
The Ubuntu login screen should then appear on the monitor.
Login to the UP Core using the credentials:
- Username: px4vision
- Password: px4vision
Developing/Extending PX4 Avoidance
The PX4 Vision's UP Core computer provides a complete and fully configured environment for extending PX4 Avoidance software (and more generally, for developing new computer vision algorithms using ROS 2). You should develop and test your software on the vehicle, sync it to your own git repository, and share any fixes and improvements with the wider PX4 community on the github PX4/PX4-Avoidance repo.
The catkin workspace is at ~/catkin_ws, and is preconfigured for running the PX4 avoidance local planner. The launch-from-boot file (avoidance.launch) is in the px4vision_ros package (modify this file to change what planner is launched).
The avoidance package is started on boot. To integrate a different planner, this needs to be disabled.
Disable the avoidance process using the following command:
shsystemctl stop avoidance.serviceYou can simply reboot the machine to restart the service.
Other useful commands are:
sh# restart service systemctl start avoidance.service # disable service (stop service and do not restart after boot) systemctl disable avoidance.service # enable service (start service and enable restart after boot) systemctl enable avoidance.serviceThe source code of the obstacle avoidance package can be found in https://github.com/PX4/PX4-Avoidance which is located in
~/catkin_ws/src/avoidance.Make changes to the code! To get the latest code of avoidance pull the code from the avoidance repo:
shgit pull origin git checkout origin/masterBuild the package
shcatkin build local_planner
The ROS workspace is placed in ~/catkin_ws. For reference on developing in ROS and using the catkin workspace, see the ROS catkin tutorials.
Developing PX4 Firmware
The kit is designed for creating computer vision software that runs on the companion computer, and which integrates with PX4’s flexible path planning and collision prevention interfaces.
You can also modify PX4 itself, and install it as custom firmware:
- You will need to connect QGroundControl to the kit's Pixhawk via USB in order to update firmware.
- Select the PX4 Vision DevKit airframe after loading new firmware:
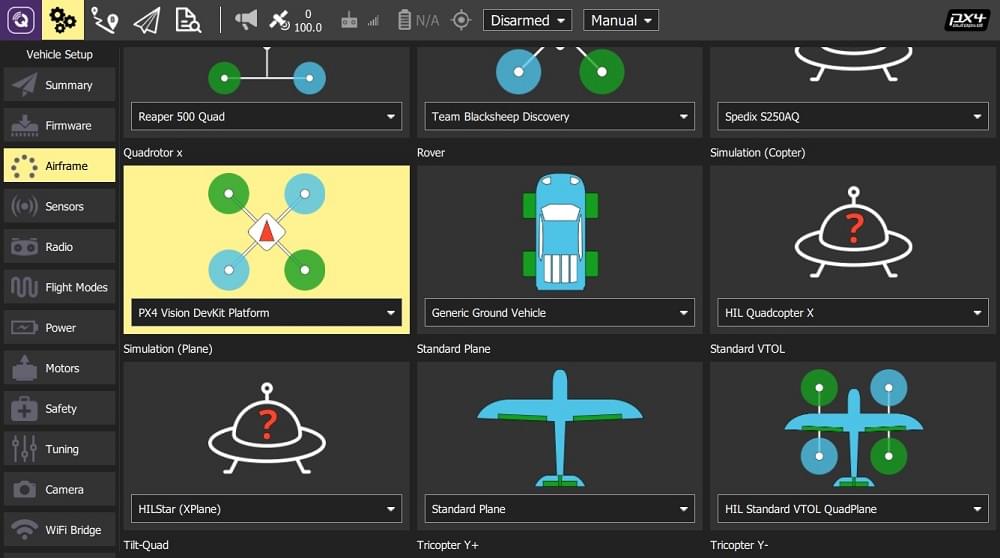
:::note Modification of PX4 code is not needed to meet most computer vision use cases. To discuss the interfaces or how to integrate other features join the PX4 support channels. :::
PX4 Vision Carrier Board Pinouts
Information for the PX4 Vision 1.15 can be found at https://docs.holybro.com. The carrier board pinouts and other information are in the downloads section.
Other Development Resources
- UP Core Wiki - Up Core companion computer technical information
- Occipital Developer Forum - Structure Core camera information
- Pixhawk 4 Overview
- Pixhawk 6C Overview
- PX4 Avoidance software/documentation
- Path Planning Interface
How to get Technical Support
For hardware issues, please contact Holybro at: productservice@holybro.com.
For software issues, use the following community support channels: